Jak używać właściwości „display” do reprezentowania tabeli?
Poniższa tabela przedstawia relację między znacznikiem „ table ” a odpowiednią obsługiwaną właściwością CSS reprezentującą ten sam element. Tak więc podczas tworzenia tabeli wszystko, co musisz zrobić, to zamiast znacznika HTML „ table ” po prostu użyć znacznika „ div ” i dodać odpowiedni kod CSS, aby wyświetlić tabelę.
| <tabela> | {wyświetlacz:stół} |
| <tr> | {wyświetlacz: wiersz tabeli} |
| <głowa> | {display: table-header-group} |
| <ciało> | {display: grupa-wierszy-tabeli} |
| <stopa> | {display: table-footer-group} |
| <kolumna> | {wyświetlacz: kolumna tabeli} |
| <grupa kol.> | {display: grupa-kolumn-tabeli} |
| <td>, <th> | {wyświetlacz: komórka tabeli} |
| <podpis> | {display: table-caption} |
Krok 1: Utwórz główny div dla tabeli
HTML
<div class="d-tbl"></div>CSS
.d-tbl {
width: 100%;
display: table;
border-collapse: collapse;
}Krok 3: Utwórz podpis tabeli, nagłówek, treść, stopkę
HTML
<div class="d-tbl">
<div class="d-tbl-head"></div>
<div class="d-tbl-body">/div>
<div class="d-tbl-foot"></div>
</div>CSS
.d-tbl-caption{
display: table-caption;
text-align: center;
font-weight: bold;
}
.d-tbl-head,
.d-tbl-foot {
display: table-header-group;
background-color: white;
}
.d-tbl-body {
display: table-row-group;
}Krok 3: Utwórz wiersze tabeli, komórkę, komórkę głowy, komórkę stopy
HTML
<div class="d-tbl">
<div class="d-tbl-head">
<div class="d-tbl-row">
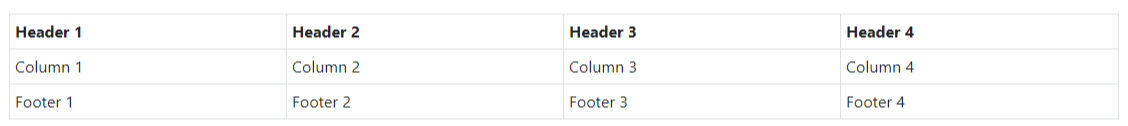
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-cell">Header 1</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-cell">Header 2</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-cell">Header 3</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-cell">Header 4</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="d-tbl-body">
<div class="d-tbl-row">
<div class="d-tbl-cell">Column 1</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell">Column 2</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell">Column 3</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell">Column 4</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="d-tbl-foot">
<div class="d-tbl-row">
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-foot">Footer 1</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-foot">Footer 2</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-foot">Footer 3</div>
<div class="d-tbl-cell d-tbl-head-foot">Footer 4</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>CSS
.d-tbl-row {
display: table-row;
}
.d-tbl-cell {
display: table-cell;
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid #dee2e6;
}
.d-tbl-head-cell,
.d-tbl-foot-cell {
font-weight: bold;
}Wynik
Krok 4: dodaj pasek przewijania do tabeli
HTML
<div class="p_fix_table">
<div class="d-tbl">
<div class="d-tbl-head" id="d-tbl-fix-head"></div>
<div class="d-tbl-body" id="d-tbl-fix-body" onscroll="tblFixScroll('d-tbl-fix-head', 'd-tbl-fix-body')"></div>
</div>
</div>CSS
.p_fix_table {
width: 100%;
max-height: 250px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex: 1 1 auto;
width: 100%;
max-height: 250px;
border: 1px solid #dee2e6;
border-collapse: collapse;
overflow: hidden;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-head {
flex: 1 0 auto;
display: block;
overflow-x: hidden;
overflow-y: scroll;
scrollbar-base-color: #dee2e6;
scrollbar-face-color: #dee2e6;
scrollbar-highlight-color: #dee2e6;
scrollbar-track-color: #dee2e6;
scrollbar-arrow-color: #dee2e6;
scrollbar-shadow-color: #dee2e6;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-head::-webkit-scrollbar {
display: block;
background-color: transparent;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-head::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
background-color: transparent;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-body {
display: block;
overflow: scroll;
max-height: 220px;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-body:nth-child(3) {
display: none;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-cell,
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-head-cell {
width: 170px;
min-width: 170px;
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid #dee2e6;
}
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-row .d-tbl-cell:first-child,
.p_fix_table .d-tbl-row .d-tbl-head-cell:first-child {
position: sticky;
left:0;
background: white;
z-index: 1;
}JS
function tblFixScroll(thead_id, tbody_id) {
let thead = document.getElementById(thead_id);
let tbodyScroll = document.getElementById(tbody_id).scrollLeft;
thead.scrollLeft = tbodyScroll;
//document.getElementById("frozen").scrollLeft = 0;
}